-
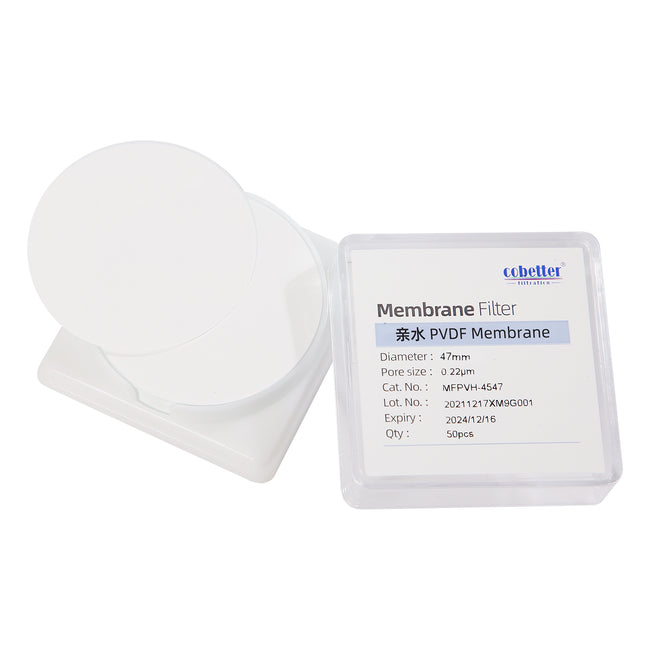

Hydrophilic PVDF Disc Membrane Filters 25/50/100 pcs/pk
Membrane Hydrophilic PVDFPore size 0.1/0.22/0.45μmPackage 25/50/100 pcs/pk -

Hydrophilic PTFE Membrane Filters Lab Disc Filter 25/50/100 pcs/pk
Membrane Hydrophilic PTFEPore size 0.1/0.22/0.45μmPackage 25/50/100 pcs/pk -

Hydrophobic PTFE Membrane Filters Lab Disc Filters 25/50/100 pcs/pk
Membrane Hydrophobic PTFEPore size 0.1/0.22/0.45/1.0/3.0/5.0μmPackage 25/50/100 pcs/pk -
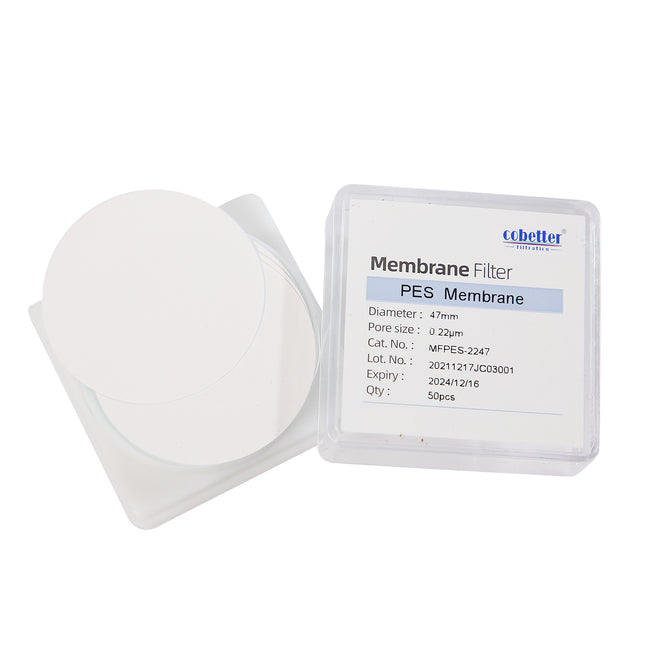

Hydrophilic PES Disc Membrane Filters 25/50/100/ pcs/pk
Membrane PESPore size 0.1/0.22/0.45/0.8/1.2/3.0/5.0/8.0μmPackage 25/50/100/ pcs/pk -

Hydrophobic Polypropylene Disc Membrane Filters 25/50 pcs/pk
Membrane PPPore size 0.1/0.22/0.45/1.0/3.0/5.0/10.0/20.0μmPackage 25/pk, 50/pk -

Hydrophilic MCE Disc Membrane Filters 25/50 pcs/pk
Membrane MCEPore size 0.22/0.45μmPackage 25/pk, 50/pk